The browser you are using is not supported. Please consider using a modern browser.

Choosing mesh counts for screen printing projects
Choosing mesh counts for screen printing projects
Choosing Mesh Counts for Every Screen Printing Project
When diving into the world of screen printing, one term you’ll hear often is mesh count. It’s not just technical jargon—it’s the secret sauce behind crisp, clean prints or a blurry disaster. Choosing mesh counts ensures that the ink flows just right, the image stays sharp, and your fabric or material doesn’t bleed or blur. So, what mesh count should you use for different projects? Let’s break it down with clarity.

Image By Lawson
What Is Mesh Count in Screen Printing?
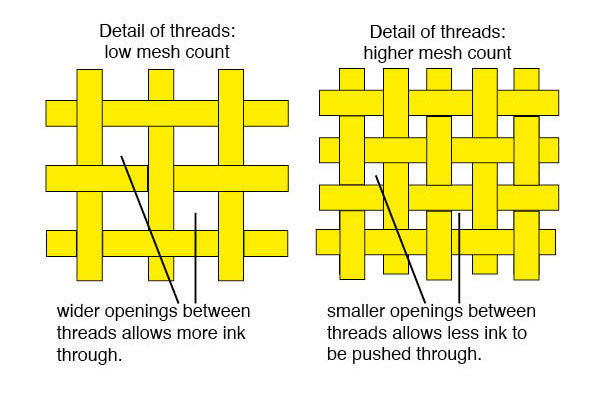
Mesh count refers to the number of threads per inch in a screen. Higher mesh counts mean more threads and smaller openings; lower mesh counts mean fewer threads and larger openings.
Why Mesh Count Matters
-
Controls ink flow
-
Impacts print detail
-
Affects durability
-
Optimizes material compatibility
Choosing Mesh Counts by Project Type
Bold Graphics and Athletic Prints
-
Recommended Mesh Count: 86–110
-
Why: These allow more ink to pass through, great for cotton fabrics and athletic wear.
Text and Fine Line Work
-
Recommended Mesh Count: 156–160
-
Why: Offers a balance between ink deposit and detail retention.
Halftones and Detailed Artwork
-
Recommended Mesh Count: 200–230
-
Why: Provides exceptional detail for photo-realistic images.
Four-Color Process Printing
-
Recommended Mesh Count: 305+
-
Why: Extremely fine mesh needed for precision and blending of colors.
Image by LCCPrintmaking
Tips for Choosing the Right Mesh Count for screen printing projects
-
Know your substrate: T-shirts, posters, and glass all need different mesh levels.
-
Match the ink type: Thicker inks = lower mesh. Thinner inks = higher mesh.
-
Consider design detail: Finer details require finer mesh.
Ready to get your custom apparel? Get in touch today! Click Here
Social Media
Check us out on Instagram
Like us on Facebook
Check in on LinkedIn